What Are the Different Types of Orthopedic Implants?
orthopedic implants are critical in modern medicine, bridging the gap between injury and healing. According to the Global Orthopedic Implant Market Report, this sector is projected to reach over $60 billion by 2025. Such growth reflects increasing advancements in technology and an aging population. These implants enhance the quality of life for many patients.
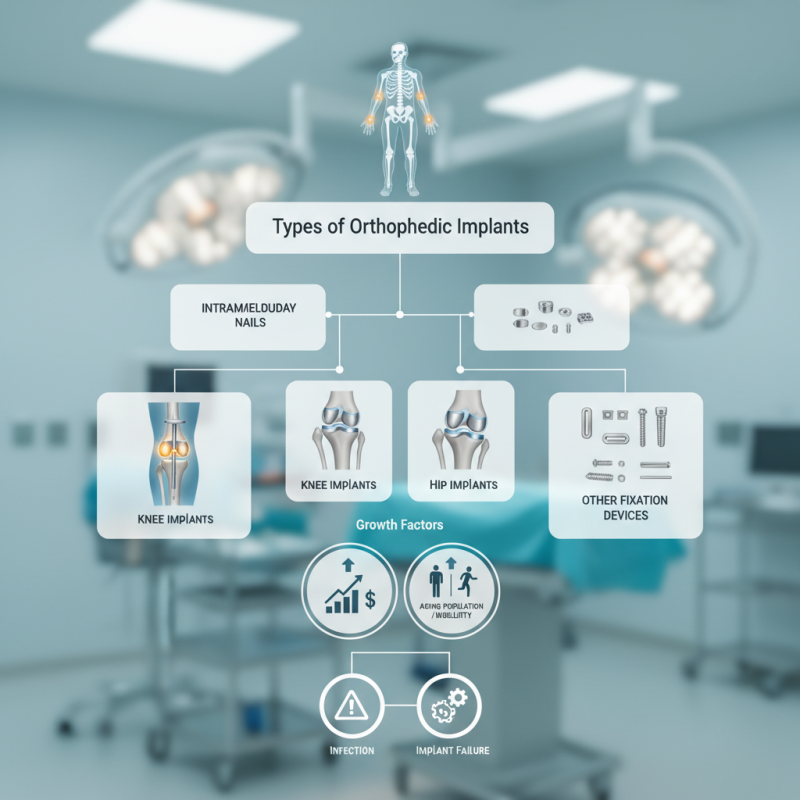
Several types of orthopedic implants exist, each serving a unique function. For instance, intramedullary nails provide stability for long bone fractures. The demand for joint replacements continues to surge, as knee and hip implants help countless individuals regain mobility. However, the selection of the appropriate implant can be complex, requiring careful consideration of patient needs and implant durability.
Despite advancements, challenges remain. Some orthopedic implants may lead to complications over time. Infection and implant failure are critical concerns that necessitate ongoing research. Continuous improvements are vital to ensure patient safety and satisfaction. Orthopedic implants are integral to orthopedic surgery, but they also require constant evaluation and refinement.
Types of Orthopedic Implants: An Overview
Orthopedic implants play a crucial role in modern medicine. They help restore function and mobility for patients with bone and joint issues. Various types of orthopedic implants cater to specific needs. These include plates, screws, rods, and joint replacements. Each type serves a unique purpose in treatment.
Plates are often used to stabilize fractures. They attach directly to the bone, promoting healing. Screws, on the other hand, secure bones in place during recovery. Rods are useful for reinforcing long bones. Joint replacements, like hip or knee implants, restore movement in damaged joints.
Despite advancements, challenges remain. Not all implants fit every patient perfectly. Complications can arise, leading to revisions. Surgeons must carefully consider factors like bone density and overall health. The choice of implant is essential but can be complex. Understanding these different types helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
Joint Replacement Implants: Purpose and Types
Joint replacement implants are crucial in restoring mobility for patients with severe joint damage. These implants can relieve pain and enhance the quality of life. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, about 1 million total knee replacements are performed annually in the U.S. alone. This figure highlights the growing reliance on these medical devices.
There are several types of joint replacement implants, such as total and partial replacements. Total joint replacements involve replacing both the damaged cartilage and bone. They are commonly used in knees and hips. Partial replacements, on the other hand, only replace one compartment of the joint. Each type has its advantages and potential drawbacks, necessitating careful discussion between patients and doctors.
An often overlooked aspect is the longevity of these implants. Many can last around 10 to 20 years, but some may require revision surgeries. Data shows that approximately 10% of patients may need another operation within a decade. This uncertainty prompts a need for continuous advancements in materials and techniques. As technology evolves, understanding these implants will remain vital for achieving better outcomes.
Fracture Fixation Devices: Plates and Screws
Fracture fixation devices play a crucial role in orthopedic surgery. Among these devices, plates and screws are the most commonly used. They provide stability and support to fractured bones, allowing them to heal correctly. Studies indicate that the global market for orthopedic implants, including these fixation devices, was valued at over $45 billion in 2021. There is growing demand for innovative solutions in this field.
Plates are flat devices that are attached to the bone's surface using screws. They offer precise alignment and stability, especially in complex fractures. However, their surgical placement requires a significant level of skill. Issues like improper positioning can lead to complications. Reports suggest that around 10% of surgeries face challenges related to misalignment or infection.
Screws, on the other hand, serve as anchors for the plates and provide additional support. They come in various designs and sizes to suit different types of fractures. A study in the Journal of Orthopedic Research showed that screw design can impact healing times. It noted that certain types of screws could reduce recovery times by nearly 20%. Nonetheless, the choice of screws can be quite overwhelming. Many orthopedic surgeons find it challenging to select the optimal configuration for their patients. This highlights the ongoing need for education and advancements in this essential area of orthopedic care.
Spinal Implants: Function and Variations
Spinal implants play a crucial role in orthopedic surgeries. These devices are designed to stabilize the spine and support healing. They are often used in conditions like spinal deformities, fractures, and degenerative diseases. The global spinal implant market is projected to reach $19 billion by 2026, showing significant growth potential.
There are various types of spinal implants, including rods, screws, and cages. Each type has its unique function, yet often surgical teams may opt for combinations. For instance, a fusion cage can promote bone growth, while screws provide stability. Despite advancements, complications can arise. The rate of revision surgeries stands at around 10% according to recent studies.
Material choices also vary. Titanium is common due to its strength and biocompatibility. However, some surgeons might face challenges with allergic reactions or fatigue failures. Ongoing research continues to refine these materials, yet some issues remain unresolved. Engaging with evolving technologies is vital, even if imperfections still exist in the current approaches.
Bone Grafts and Substitutes in Orthopedic Surgery
Bone grafts and substitutes play a crucial role in orthopedic surgery. They aid in healing fractures and reconstructing damaged bone. Traditional grafts often come from donors. These human tissues provide vital cells for regeneration. However, there are potential risks, like infection or rejection.
Synthetic bone substitutes have gained popularity. These materials mimic natural bone structure. They can be made from ceramics or polymers. Some options are more effective than others. The challenge lies in the biological response. Not all substitutes promote bone growth equally. Surgeons often have to weigh pros and cons.
In some cases, bone grafts may not integrate well. This could lead to complications. Therefore, continuous research is essential to improve these solutions. As medical technology evolves, so does the potential for better treatments. Each case requires careful consideration. The goal is always optimal healing.